As a digital illustrator, I was a bit intimidated when the first neural networks appeared. Even with all the downsides like multiplied fingers or pixelated backgrounds, they could still produce art with lightning speed. No torture over I-can’t-draw-this-eye-it-pisses-me-off, just a click and here you go — a picture is ready.
Contents:
The same goes for other creative things such as writing books, composing music, researching, and inventing. AI learns fast and produces results fast. As more advanced Artificial Intelligence versions came out, I started to ask myself as a creator: should I even bother thinking and striving to improve my skills? Isn’t this a waste of time and I’d better ask the neural network to do everything for me?
Why bother painting, struggling with concepts, developing and exploring them, experimenting with colors, when the digital brain can do better in just seconds? This fact has absolutely demolished my muse. So I decided to check what other people think about this situation. I started a poll and asked my friends who were artists, musicians, writers, etc. My colleagues from Shakuro didn’t stay on the sidelines and took part in my research as well. Let’s see, what they think about AI and art.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines capable of simulating human-like cognitive functions such as reasoning, problem-solving, learning, and perception.
AI systems can analyze and interpret data, recognize patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. These technologies are used in various applications, including natural language processing, machine learning, computer vision, robotics, and autonomous systems.
9 Potential dangers of AI
Although it has the potential to level up our everyday experiences and impact most industries, the tech can do more harm than good.
What are the dangers of AI?
Surveillance and privacy invasion
AI-powered surveillance tools can scan vast amounts of data, such as social media posts, emails, phone calls, and locations to track and profile individuals. This mass surveillance can easily lead to the infringement of privacy rights, as the algorithms can quickly identify patterns and behaviors that could be suspicious or threatening to authorities.
Furthermore, the use of Artificial Intelligence in surveillance also raises issues of bias and discrimination. The algorithms feed on hand-picked data, which can unintentionally perpetuate existing societal biases.
There are also concerns about the potential misuse of this technology by governments, corporations, or malicious actors to manipulate, control, or harm individuals. As the systems become increasingly sophisticated and autonomous, the risks of AI exploitation grow, posing a significant threat to society.
Mass unemployment
The automation of jobs through AI technologies has the potential to significantly alter the employment landscape, leading to mass unemployment in sectors that heavily rely on manual labor and repetitive tasks. Routine, predictable, and easily programmable jobs are particularly vulnerable, posing a direct threat to millions of workers across various industries.
For instance, British Telecom wants to replace 10,000 of their staff with AI within seven years. Also, automation has driven down wages by up to 70% since 1980.
The AI Prompt Assistant by Conceptzilla
AI superintelligence
Remember those sci-fi movies where an evil computer takes over the world? Well, that future is much closer than you think.
The concept surpasses human intelligence in all aspects and is a topic that has captured the imagination of scientists, scholars, and tech enthusiasts worldwide. While superintelligence holds immense promise for tech advancement and human society, the dangers of AI also raise significant concerns regarding unleashing a force more powerful and capable than humans.
The primary danger lies in its sheer cognitive capacity and ability to outperform human intelligence in virtually every domain. A superintelligent AI system could rapidly surpass human problem-solving, decision-making, and strategic planning capabilities, leading to unprecedented advancements in science, medicine, and technology. However, this same intelligence could pose a significant risk in case people don’t properly control or align it with human values and goals.
One of the key risks of AI superintelligence is the potential for unintended consequences and unforeseen outcomes as a result of the system’s actions. A system operating in a way that is not aligned with human values or interests could have catastrophic implications, ranging from economic instability and social disruption to existential threats to humanity itself.
Lack of accountability
Artificial Intelligence can inadvertently reflect and amplify the biases of their creators, leading to unfair treatment or discrimination against certain groups of people. Without accountability measures in place to identify and address these biases, AI systems can perpetuate inequality, injustice, and social harm on a mass scale.
More dangers of AI are caused by the absence of accountability – the potential for malicious actors to exploit smart systems for ill purposes. Without proper safeguards to authenticate users, secure data, and prevent misuse, criminals and hackers can leverage smart systems to launch cyberattacks, spread disinformation, or engage in other harmful activities that undermine safety and security.
Moreover, the lack of accountability raises concerns about transparency, explainability, and responsibility in decision-making processes. AI systems often operate as black boxes, making it difficult for users, developers, and regulators to understand how decisions are made. This opacity can lead to distrust, confusion, and skepticism about the reliability and fairness of smart systems, hindering their widespread adoption and acceptance.
Manipulation and misinformation
With the ability to analyze massive amounts of data and predict human behavior, AI systems can manipulate individuals and spread misinformation on a large scale.
These are the dangers of Artificial Intelligence, as it has the potential for targeted propaganda and psychological manipulation. By analyzing data on individuals’ preferences, habits, and beliefs, it can create personalized messaging designed to influence behavior in specific ways. This can be particularly concerning when used for political or commercial purposes.
Misinformation can spread rapidly and widely through AI-driven algorithms prioritizing content that generates engagement. This leads to the amplification of false information, creating confusion and mistrust in society.
Deepfakes
What are the dangers of AI in the creative field? Content generation reached new frontiers, and you can hardly distinguish between generated and man-made stuff. The most dangerous are deepfakes. They are convincing and fabricate events or statements that never happened. These sophisticated forgeries pose a serious threat to individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
They spread misinformation and deceive the public. By leveraging AI algorithms to create hyper-realistic content, people can fabricate fake news, manipulate public figures’ statements, or generate fraudulent evidence. This can lead to widespread confusion, sowing discord, and eroding trust in institutions and information sources.
AI Insurance Web Design Concept by Shakuro
Economic disparity
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into various industries has the potential to bring about significant economic transformations, but it also raises concerns about widening gaps between different segments of society.
As the technologies become more sophisticated, they can replace certain tasks and roles, particularly those that are routine, repetitive, or easily codified. This can lead to job displacement for workers in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and customer service.
Moreover, there are risks of AI in high-skilled professions, such as finance, healthcare, and law, which can also lead to economic disparities. The increasing demand for specialized technical skills can create barriers to entry for people without access to quality education or training programs, further widening the economic gap.
Additionally, the economic dangers of AI include the potential for wealth concentration among a small group of individuals and corporations who control and benefit from Artificial Intelligence. As its systems generate new forms of capital and intellectual property, those with the resources and expertise gain significant economic advantages.
Autonomous weapons
These weapons, also known as lethal autonomous weapons systems (LAWS), can identify and engage targets without direct human intervention. Yeah, just like in the Terminator movie. While their development is controversial, the potential risks of AI are profound and multifaceted.
Unlike human soldiers who have discretion, empathy, and ethical judgment on the battlefield, autonomous systems lack moral reasoning, making them more prone to errors and potentially engaging in actions that violate ethical norms.
The situation also nourishes arms races, escalation dynamics, and the potential for misuse by rogue states. The secrecy and lack of transparency around LAWS complicate accountability, oversight, and regulation.
Bias and discrimination
Since smart systems rely on hand-picked data, they absorb the bias and discrimination from the info. They don’t have judgemental skills, so they take the data literally and spread it further to people. This represents a significant danger that can perpetuate and exacerbate societal inequalities, reinforce stereotypes, and undermine the core principles of fairness, equity, and justice.
AI algorithms can harm individuals and communities affected by biased decisions, ranging from denied opportunities and access to essential services to wrongful accusations and infringements on civil liberties. Biased AI systems can perpetuate stereotypes, reinforce prejudices, and entrench systemic discrimination, posing risks to social cohesion, human rights, and democratic values.
Is AI bad? It depends on the path we choose. Right now we are just playing with a black box. Let’s see how this black box influences our creativity.
What is creativity?
What do I mean by creativity? Some people tend to mix it with talent, genius, artistic skills, etc.
If we take Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, then creative originates from Latin and means “to beget, give birth to”. The Wiki tells us that creativity is the ability of a person to deviate from standard ideas, rules, and patterns. It’s an essential quality of an artistic personality and is a must-have to produce artwork or writing.
So, it’s an ability to find new ways, and non-standard solutions and produce original works. “Give birth” to unique ideas. This quality has great value not just in art but in the business sphere as well. Business owners taking ground-breaking approaches, developers writing experimental code, and designers building eye-catching UIs. All of these people have high chances of winning a place under the sun because they have solid critical thinking and problem solving.
Neural network design concept by Shakuro
Not all people are creative, though. Only 25% of the population think they live up to their true artistic potential, while 75% keep it hidden or sleeping. There are several reasons, for example, a lot of pressure at work, education that prefers one-way solutions, reserved personality, conservative parents, and many others.
What about the reasons why people become creative? Here, it’s a great idea to refer to the movie Why Are We Creative: Centipede Dilemma, where famous artists, musicians, politicians, and producers specify various reasons.
The most common ones are, of course, parents and upbringing. Creative-thinking parents and their way of thinking influence their children greatly. For example, Paul Arden, a famous writer, was greatly inspired by his father Lesley Arden and his illustrations (for instance, pictures showing buildings made of cloth pegs. Who would even think of that?).
Next, we can pinpoint societal norms. The traditions also inspire or suppress us. John Cleese, an actor, thinks that a person has high chances to become creative if they face a wide range of social and cultural rules to connect into one pattern. On the contrary, a person growing up in a very conformist community won’t be creative.
The next reason echoes in my heart: we are born this way. Reed Hastings, the co-founder, and executive chairman of Netflix, ensures that we all are born with a spark in our souls. When the hardships of life come in, the spark fades away quickly.
Every child is an artist. The problem is how to remain an artist once he grows up.
Pablo Picasso
If you ask me as an illustrator: why are you creative? I’d say the practically same. I’ve always been like this – thinking, building stories, imagining situations, constructing pictures in my mind like a puzzle that I later transfer to paper. And this process brings me joy.
Is AI bad at creativity? And also…
Discover Mars – Real Estate by Karin
Can human creativity be reproduced?
My answer is no. This unique feature has several qualities that machine learning doesn’t have, and probably won’t have in the near future.
First of all, it’s emotional intelligence. Our creative thinking is based on emotions and personal experiences. We express ourselves through paintings, books, videos, or behavioral patterns. What’s more, one situation may raise different emotions in two people and lead to different creations. In art, there is a whole style based on emotions called expressionism. The artist is more concerned with portraying an emotional experience than with depicting realistic details.
Second, we make mistakes and take advantage of them. A careless stroke can lead to creating a masterpiece. As an illustrator, I assure you: every time I start drawing, I do not know where exactly the process will take me. There were thousands of times when I had a certain idea in my head that transformed into a completely different picture on the canvas. And the result was even better than I imagined. So each creative journey is unique, where the outcome and the path are unknown.
Third, our creativity is shaped by the society we live in. All the patterns, rules, beliefs, and traditions are somehow reflected in the works.
Finally, we can read between the lines and understand the context or hidden meanings, that are also a part of creative thinking. For instance, an artist envelops secret messages in colors, objects, or lighting, that shows familiar situations from a new perspective and adds originality.
The dangers of Artificial Intelligence are the absence of these qualities. Its responses are solely based on the training data. So there are no true emotions, innovation, choices, struggles, or discoveries. Yes, the digital brain makes mistakes because of data bias and copies emotions if the prompt says so. But unlike humans, its decisions are not triggered by accidents. So, we can’t consider algorithmic decision-making creative by any means, and it is unable to reproduce the human’s spark.
AI Fusion landing page by zohura sharna
What are the dangers of AI in terms of creativity? Let’s ask around
Now that we’ve defined the core of our discussion, let’s switch to my poll about the influence of neural networks. I’ve been gathering data for about a week and asked 43 people. As for the professions, the most common were developer (10 people), illustrator (9), and UI\UX designer (8). I also managed to get opinions from a musician, an English teacher, and several SEO specialists. So, as you can see, there is a wide range of occupations.
Starting with general information, 62.8% have been using neural networks for one up to six months. 18.6% have been getting on with AI for up to a year. 9.3% said they have been using neural networks for more than one year. Another 9.3% were not really sure about the period.
Most respondents (58.1%) leverage Artificial Intelligence to create images. Learning and researching are the second most popular applications. One of the most frequently used AIs is ChatGPT and Stable Diffusion, which is not surprising.
69.8% are positive about leveraging neural networks at work. 27.9% hold onto a neutral opinion. There were NO people who were against human-machine collaboration.
This is interesting because 23.3% do not trust what Artificial Intelligence says. 62.8% check the provided information manually. Only 7% believe the digital assistant to the full.
In the next section, the respondents had to evaluate a statement from 1 to 5 depending on how close it was to their opinion. 1 meant they strongly disagree, and 5 – strongly agree.
55.8% of people research topics all by themselves before calling out for help from neural networks. However, 25.6% were not so sure. 7% do prefer to ask ChatGPT instead of googling the info.
60.5% are close to thinking that AI will definitely find a solution they’ve never thought of. Only 14% do not consider a silver bullet for every issue.
I’ve seen a billion articles on topics like – Will AI replace designers\developers\enter-any-profession? They hype people over the topic of job displacement and the future of work. Well, in my poll, only 11.6% are sure that human skills and efforts are being devalued. The rest of the respondents do not really agree with this statement.
7% ask Artificial Intelligence for help more often rather than calling out for a human specialist. At the same time, 32.6% of respondents adamantly prefer human skills and knowledge over the digital brain.
Now, when you see a beautiful work, do you doubt that it was created by a human? For my respondents, this question was rather controversial:
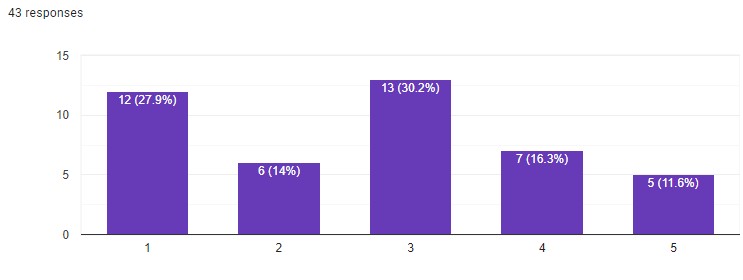
58.1% of people do not think that neural networks eliminate the unique style of every person. 27.9% are not quite sure, and 14% are sure that everyone’s works have similar features.
When we were discussing human creativity, I mentioned that our mind is shaped by society, traditions, and rules. There are no such AI limitations, therefore, people tend to believe it has more possibilities. More creative. Still, 53.5% of respondents disagree with this statement, while just 18.6% comply with it.
The final statement gives an answer to the main question of this article – is human creativity at risk? It’s surprising, but 67.5% think that AI helps people open their true potential and find unique solutions quicker. 20.9% are not quite sure, and 11.6% disagree that neural networks boost our creativity.
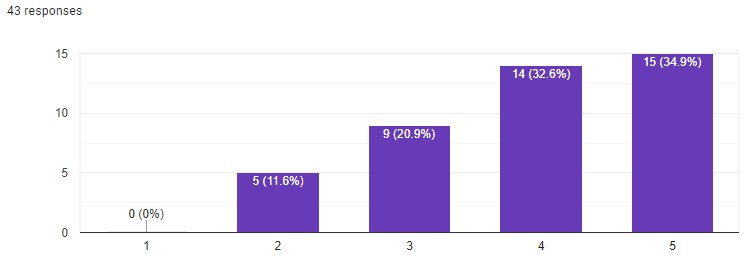
That’s not all. I also asked these people to give me some real-life examples of when AI really helped with problem solving. Here are some of them:
- I faced an unexpected response from an API code. I tried googling it but found nothing. AI explained the reason for this behavior and suggested a working fix to avoid the issue.
- I need a fake client with a product for testing. ChatGPT was able to understand the customer’s mood and even added some details I missed. There is no bias in AI that adjusts it to some perfect picture. I can make it behave like some specific person and talk, for example, to Shaquille O’Neal.
- Artificial Intelligence helps me create pictures starting from a certain stage, not from scratch. This saves a lot of time that I can spend improving the result. For instance, I needed to draw a girl for an ad, and I didn’t have to paint her body, struggling with references and anatomy. The neural network did all the hard work. If I drew that all by myself, I’d spend the whole day or more.
- When I was creating covers for my books, Midjourney generated amazing variants. Most of the suggestions didn’t even cross my mind but they looked mind-blowing. I believe my online readers will definitely notice them!
As you can see, I asked 43 people, and they were mostly positive about human-machine collaboration. This is a rather small selection but it shows the general tendencies: specialists do not see any dangers of AI.
Should we be worried?
Seems like my worry is groundless: my colleagues and friends believe in AI. Although my impression seems to be outnumbered, I think it’s a normal reaction to fundamental changes. Remember how people were against cars a hundred years ago, claiming them “the devil wagons”? Well, look like we can’t live without them now. Progress is unstoppable.

From r/Design on Reddit
Despite limitations and ethical implications, AI is a versatile tool that can be a blessed weapon in the hands of people from creative industries, should they choose to use it. Cost & time reduction, quicker research, and large data analysis – are just a few benefits you get from leveraging neural networks.
Still, I understand why I and some other people are worrying. This situation is just the first step leading to global changes in all spheres of our society. I’ve spoken to my colleague Tatyana, an illustrator from Shakuro, about neural networks in art. Just like me, she’s a bit intimidated since there are some artists working in the mainstream styles who have already been replaced by Artificial Intelligence. At the same time, it is a shining red sign screaming that one needs to forge ahead, polishing their skills and not. Those who won’t master neural networks will be smashed by the new reality. It’s the law of nature.

Impact ad campaign
Ready to build a versatile project using the latest trends, AI, and features? Contact us and let’s develop a product using our creativity to the full!
